Microinverters vs String Inverters vs Hybrid Inverters vs off Grid Inverter, How to choose?
You must know what is an inverter?

Solar Photovoltaic Inverter or PV Inverter, referred to as inverter, is a device that converts direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. It is mainly used to convert the DC power generated by solar photovoltaic panels into AC power to meet the electricity needs of households, industries and businesses.
PV inverter is one of the important devices in photovoltaic power generation systems. It not only has the function of direct-to-alternating current conversion, but also has the function of maximizing the performance of solar cells and system fault protection. In summary, there are automatic operation and shutdown functions, maximum power tracking control function, anti-is landing function (for on grid systems), low voltage ride-through function (for On grid systems), DC detection function (for On grid systems), and DC grounding detection function (for on grid systems).
Hybrid Inverter
hybrid inverter is a device that combines solar panels, utility power, and energy storage batteries into one power system, which enables the intelligent processing of power from solar panels, batteries, and the utility grid at the same time. According to the settings of the hybrid inverter, different power sources are used intelligently. The mode is dynamically switched according to the power generation and power consumption to keep the entire system running optimally.
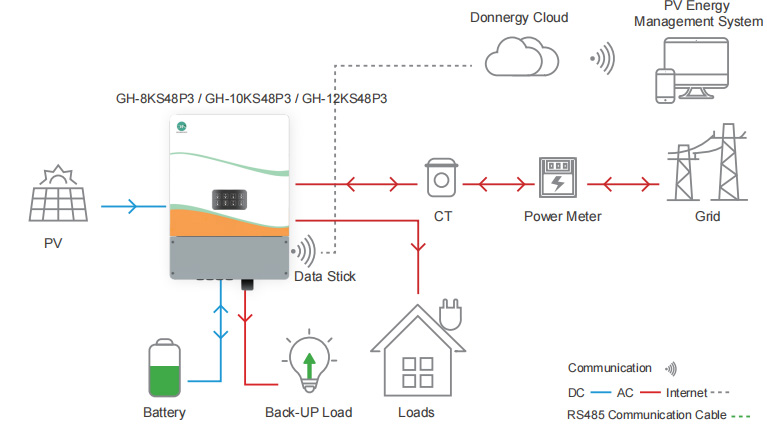
Advantages of hybrid inverters
- Battery storage can be used to provide electricity for the home in the event of a power outage;
- The power stored in the battery can be used for nighttime electricity consumption;
- Excess power can be sold to the grid, thereby achieving energy sharing and conservation.
Disadvantages of hybrid inverters
- The installation cost is high, and an additional battery energy storage system needs to be installed;
- The maintenance cost is high, and components such as batteries need to be replaced regularly;
- For some larger homes and businesses, hybrid inverters may not be able to meet their electricity needs.
Hybrid inverter applicable scenarios
- Households consume a lot of electricity and need to store electricity for nighttime use and power outage backup;
- Enterprises need energy storage to deal with emergencies such as power grid failures;
- In the case of power shortage or power restriction, a self-sufficient energy system is needed.
String Inverter

string inverter is connected to a string of solar panels, which is called a solar array. There are many ways to connect a string of solar panels. A typical solar array usually consists of N solar panels, each with a power of 200-400W. Each solar panel is connected in series with a string inverter. The inverter combines all the DC power received from each individual solar panel and immediately converts it to AC power. The number of solar panels that can be connected to a string inverter depends on the input voltage rating of the inverter.
String inverters are usually installed in a central location, usually close to the distribution board of a home or business. They convert the DC power emitted by a string (or multiple strings) of solar panels into AC power.
Advantages:
- Lower initial cost: Generally, its upfront cost is lower than that of microinverters.
- Simple: There are fewer components to install and maintain.
Disadvantages:
- Shading effect: If one panel is shaded or performs poorly, the performance of the entire string will be reduced unless a power optimizer is added.
- Less flexibility: Adding solar panels is more complicated when more power generation is needed, and may require additional or new inverters.
- Shorter warranty: Usually shorter than that of microinverters.
- Less precise monitoring: Usually only monitors the performance of the entire system, not individual panels.
Applicable scenarios
- Commercial and industrial, large residential solar system power generation needs;
- Utility-scale solar power plants;
- Hybrid solar systems;
- Microgrid systems.
Microinverter

Solar microinverter is a device in photovoltaic power generation system, generally refers to the inverter with power less than or equal to 800W and component-level MPPT in photovoltaic power generation system, and its full name is micro photovoltaic on grid inverter. “Micro” is relative to the traditional centralized inverter. The traditional photovoltaic inverter method is to connect all the DC power generated by photovoltaic cells under sunlight in series and parallel, and then use an inverter to invert the DC power into AC power to connect to the grid; the microinverter inverts each component. Its advantage is that it can independently control the MPPT of each component, which can greatly improve the overall efficiency, and at the same time avoid the DC high voltage, poor weak light effect, and barrel effect of centralized inverters.
As shown in the figure, Donnergy GT serial micro Inverter has 2MPPT, 1 in 1, 2 in 1, Single phase, 99.76% efficiency features
Advantages:
- The output power of the microinverter is proportional to the power of the solar panel. The MPPT built into the inverter can collect, control, and output the maximum power point of the solar panel, thereby improving the power generation efficiency of the system.
- Microinverters are lightweight, small, and easy to install.
- Because each microinverter outputs AC power independently, there will be no situation where the inverter group cascades and stops generating power.
Disadvantages:
- The cost of microinverters is relatively high, and each solar panel requires a microinverter, which is expensive.
- When the voltage of the power system is balanced, the microinverter may amplify the AC noise, which will eventually affect the performance of the system.
- The loss of the microinverter is large, and the power generation efficiency is generally only about 95%.
Usage scenarios
- The solar panel is not exposed to enough light for a certain period of time and range;
- There is a small demand for electricity;
- The cost of electricity is high during the peak period of the power grid.
Off Grid Inverter
Off Grid Inverter works very similarly to the above principle. The core point is that when the solar panel cannot generate enough electricity to charge the energy storage device, it will automatically switch mode to access the grid to charge the energy storage device, and the off-grid system is given priority.

Advantages:
- Off-grid inverters allow you to store the abundant energy of solar energy in batteries. At night, it uses the stored energy to power the house.
- Off-grid inverters allow you to be self-sufficient in electricity. This means that power outages or failures will not affect you.
- No longer need or pay less electricity bills because the power system does not need to use grid power all the time.
Disadvantages:
- If there is not enough sunlight, your battery may not be fully charged and there may be a power outage.
- It may be expensive to purchase and install this inverter system.
Off Grid Inverter applicable scenario:
- Stable power supply is required;
- Sunny places, far away from the public power grid, or insufficient power supply from the grid.
Microinverters vs String Inverters vs Hybrid Inverters vs off Grid Inverter, How to choose?
| Item | Shopping Cost | Maintenance costs | System scalability | System Adjustability | Main user types |
| Hybrid Inverter | high | medium | low | low | Medium, continuous and stable power demand |
| String Inverter | high | low | low | low | Meet high power demand in some areas |
| Microinverter | low | high | high | high | Complex environment with power generation demand |
| Off grid Inverter | medium | medium | medium | low | Continuous and stable power demand |




